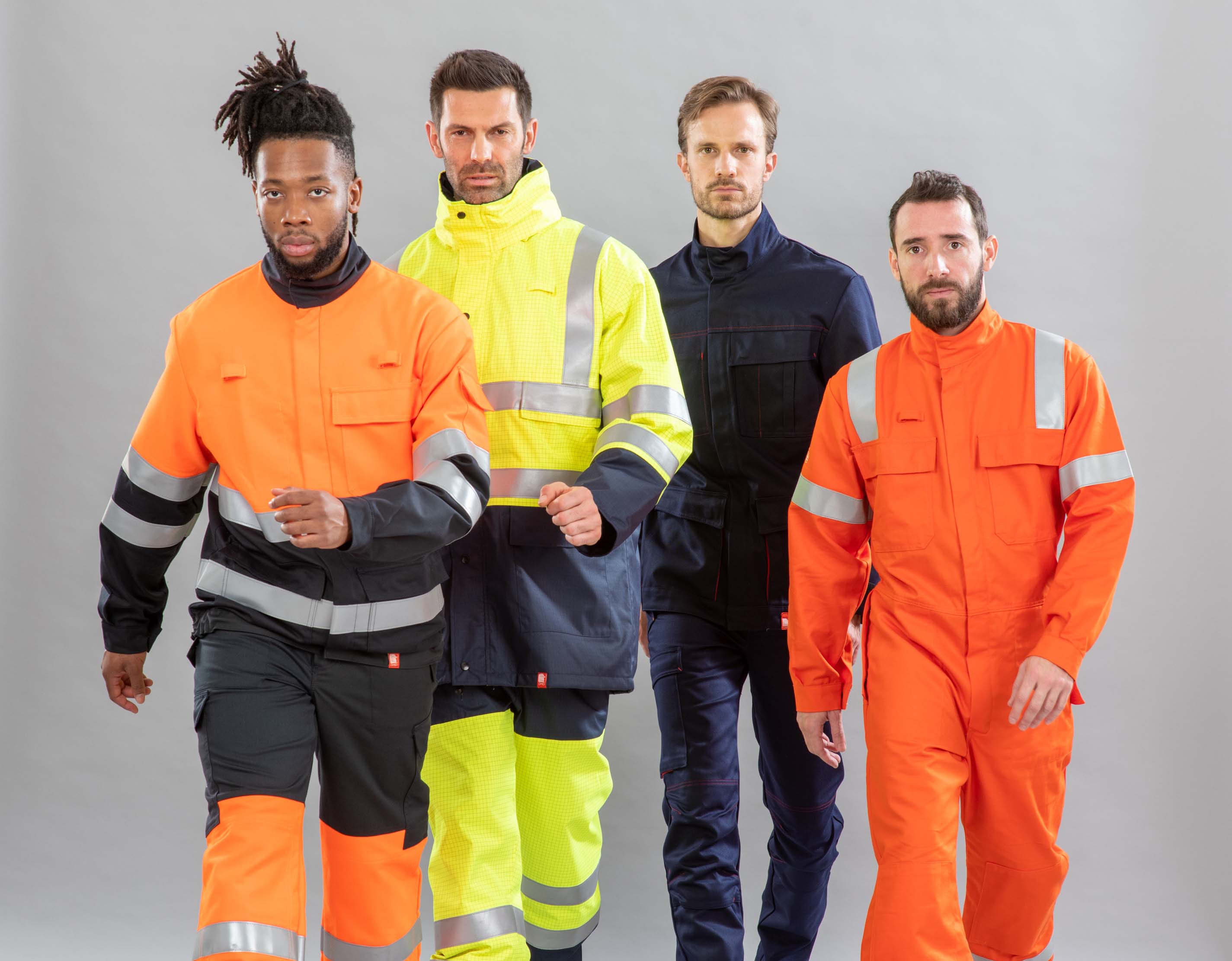
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is governed by Regulation (EU) 2016/425 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 9 March 2016 to meet the essential health and safety requirements of workers exposed to one or more occupational hazards. This regulation defines the hazards to which adapted PPE must be associated, and the procedures for placing products on the market, with the creation of the EU type-examination application and other associated documentation.
In accordance with legislation, PPE is subject to EU type-examination by a notified body. Each garment comes with a sewn-in PPE sticker and instructions for use guaranteeing its compliance with the requirements of the claimed standards and the essential provisions of Regulation 2016/425.
Regulation 2016/425 defines 3 categories of PPE according to the hazards involved:
PPE designed to protect against minor hazards whose effects have no impact on the user’s health (e.g. superficial injuries).
For these PPE, the manufacturer self-certifies the PPE by drawing up a file documenting the field of protection claimed, to attest to the PPE’s conformity with the field of protection claimed (test report, technical data sheet, CE marking).
PPE designed to protect against major hazards that can cause irreversible effects. These are known as “intermediate” hazards.
Example: high-visibility, cold, welders, etc.
These more complex PPE items are tested for compliance with European standards by an authorized body. After validation, the notified body issues the manufacturer with an EU Type-Examination Certificate (TEC)
PPE designed to protect against serious, irreversible and lethal hazards.
Example: protection against large splashes of molten metal, chemical protection, protection against the thermal hazards of electric arcs, etc.
In addition to being tested for compliance with European standards by an authorized body, these PPE are subject to mandatory annual quality control based on a choice of 2 modules:
All PPE conforming to the European standard must be clearly and fully marked. It must be supplied with instructions for care and use.

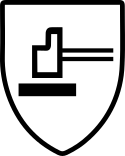 EN ISO 14404
EN ISO 14404
PPE Category 2
Knee protection
 EN 17353
EN 17353
PPE Category 2
Enhanced visibility garments for medium-risk situations
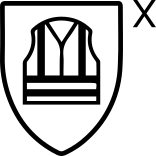 EN ISO 20471
EN ISO 20471
PPE Category 2
High-visibility clothing
 EN ISO 11612
EN ISO 11612
PPE Category 2 or 3
Clothing to protect against heat and flames
 EN ISO 11611
EN ISO 11611
PPE Category 3
Protection from welding and similar processes
 IEC 61482-2
IEC 61482-2
PPE Category 3
Protection against thermal hazards of an electric arc
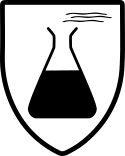 EN 13034
EN 13034
PPE Category 2 or 3
Protection against liquid chemicals type 6 and type PB[6]
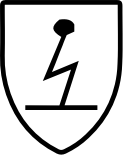 EN 1149-5
EN 1149-5
PPE Category 3
Protection against electrostatic discharge
 EN 343
EN 343
PPE Category 2
Rain protection
 EN 14058
EN 14058
PPE Category 2
Protection against cool environments
 ATEX ZONES
ATEX ZONES
ATEX directives
Managing hazards in explosive atmospheres